Crankshaft position sensor: Difference between revisions
(update) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== | ==Crankshaft position sensor== | ||
{| | {| | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
It monitors the engine crankshaft position and speed and is one of the most important input sensors that is used by the Engine Control Unit (ECU). It sends information about the position of the crankshaft and speed of the engine RPMs to the ECU which is then used to fire the spark plugs and to adjust the fuel mixture. | It monitors the engine crankshaft position and speed and is one of the most important input sensors that is used by the Engine Control Unit (ECU). It sends information about the position of the crankshaft and speed of the engine RPMs to the ECU which is then used to fire the spark plugs and to adjust the fuel mixture. | ||
==Issues | ==Function== | ||
<!-- GF07.04-P-4116-01F, Crankshaft position sensor function --> | |||
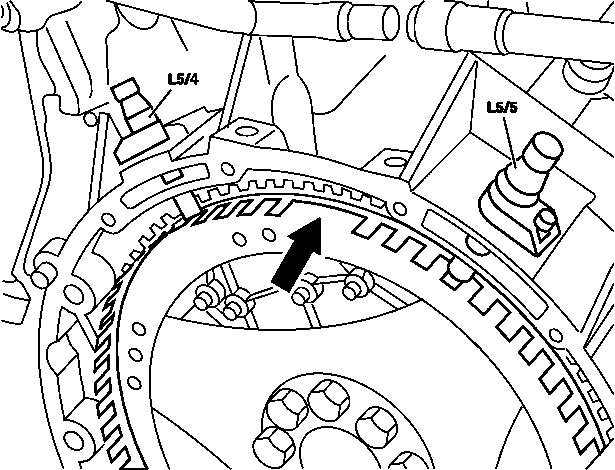
Shown on engine 120: | |||
{| | |||
|[[File:W220_crankshaft_position_sensor_function.png]] | |||
| | |||
* L5/4 - Left CKP sensor | |||
* L5/5 - Right CKP sensor | |||
|} | |||
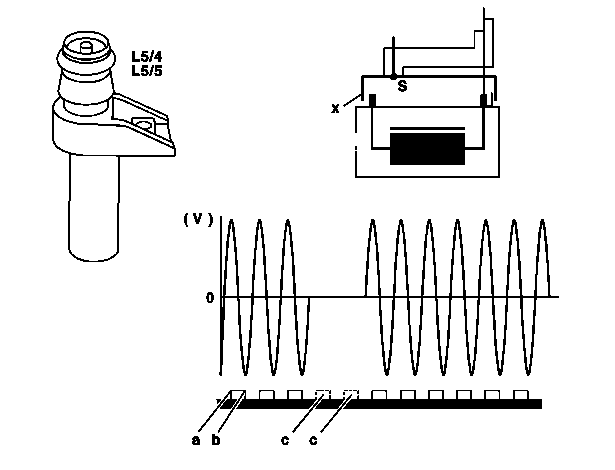
Crankshaft position and engine speed are detected contactlessly. | |||
The distance between crankshaft position sensor | |||
and the teeth of the driven plate is fixed by the installation position. | |||
When the crankshaft is rotating, an alternating voltage is generated in the | |||
crankshaft position sensor by the teeth of the driven plate. | |||
{| | |||
|[[File:W220_crankshaft_position_sensor_function2.png]] | |||
| | |||
* L5/4 - Left CKP sensor (e.g. engine 120) | |||
* L5/5 - Right CKP sensor (e.g. engine 120) | |||
* a - Leading edge of tooth | |||
* b - Trailing edge of tooth | |||
* c - 2 missing teeth (gap) | |||
* s - Screening | |||
* x - Wiring diagram illustration of the position sensor | |||
* Crankshaft with 2-pin coax-Plug contact | |||
|} | |||
The leading edge of a tooth generates a positive voltage pulse | |||
and the trailing edge a negative voltage pulse. | |||
The distance from the positive to the negative voltage | |||
peak corresponds to the length of a tooth. | |||
The gap produced by 2 missing teeth results in no voltage being | |||
generated in the crankshaft position sensor. | |||
This is analyzed for detecting the TDC position: | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
! Engine | |||
! Recognition of TDC position of cylinder | |||
|- | |||
|111 | |||
|1 and 4 | |||
|- | |||
|119, 104, 112, 113 | |||
|1 and 6 | |||
|- | |||
|120 | |||
|Right hand cylinder bank: 1 and 6; Left cylinder bank: 7 and 12. | |||
|- | |||
|137 | |||
|1 and 7 | |||
|} | |||
==Issues== | |||
M-B CPS often fail completely or become intermittent. If the crankshaft position sensor fails, it will not send information about the position of the crankshaft and speed of the engine RPMs to the ECU. As a result, the ECU doesn't know when to fire the spark plugs and how to adjust the fuel mixture. This can cause your car to stall or hesitate to start. | M-B CPS often fail completely or become intermittent. If the crankshaft position sensor fails, it will not send information about the position of the crankshaft and speed of the engine RPMs to the ECU. As a result, the ECU doesn't know when to fire the spark plugs and how to adjust the fuel mixture. This can cause your car to stall or hesitate to start. | ||
| Line 26: | Line 81: | ||
Often when the car gets hot, the sensor gets hot and the sensor's resistance goes open circuit, thus the car dies. Once the engine and sensor cool down, and if you are lucky, the resistance may come back into spec, thus the car starts again. | Often when the car gets hot, the sensor gets hot and the sensor's resistance goes open circuit, thus the car dies. Once the engine and sensor cool down, and if you are lucky, the resistance may come back into spec, thus the car starts again. | ||
==Fault Codes | ==Fault Codes== | ||
If your check engine light is on, then your ECU has recorded some sort of trouble code. You can check these codes with a diagnostic scan tool. | If your check engine light is on, then your ECU has recorded some sort of trouble code. You can check these codes with a diagnostic scan tool. | ||
| Line 57: | Line 112: | ||
|} | |} | ||
==Part Numbers | ==Part Numbers== | ||
W220 uses magnetic impulse triggering sensor with two wires. | W220 uses magnetic impulse triggering sensor with two wires. | ||
* CPS OE A0031532728 (Replaced by A0031532828) | * CPS OE A0031532728 (Replaced by A0031532828) | ||
| Line 74: | Line 129: | ||
|} | |} | ||
==DIY Tests | ==DIY Tests== | ||
The CPS can be tested by measuring its resistance and checking whether it generates voltage. | The CPS can be tested by measuring its resistance and checking whether it generates voltage. | ||
| Line 97: | Line 152: | ||
|} | |} | ||
==DIY Replacement | ==DIY Replacement== | ||
{| | {| | ||
|[[File:E8_torx_socket.jpg|thumb|none|Torx screw in E8 torx female socket.]] | |[[File:E8_torx_socket.jpg|thumb|none|Torx screw in E8 torx female socket.]] | ||
| Line 128: | Line 183: | ||
|} | |} | ||
== Resources | == Resources== | ||
* http://www.doityourself.com/stry/warning-signs-of-a-bad-crankshaft-position-sensor | * http://www.doityourself.com/stry/warning-signs-of-a-bad-crankshaft-position-sensor | ||
* http://www.mercedesmedic.com/crank-shaft-position-sensor/ | * http://www.mercedesmedic.com/crank-shaft-position-sensor/ | ||
Revision as of 10:45, 24 February 2017
Crankshaft position sensor
 |
 |
 |
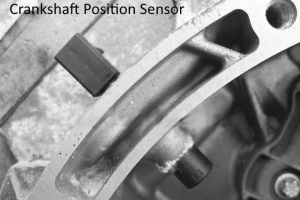
The crankshaft position sensor (CPS) is located on car's left side, towards the rear of engine. Back of engine, near the firewall. It monitors the engine crankshaft position and speed and is one of the most important input sensors that is used by the Engine Control Unit (ECU). It sends information about the position of the crankshaft and speed of the engine RPMs to the ECU which is then used to fire the spark plugs and to adjust the fuel mixture.
Function
Shown on engine 120:
|
|
Crankshaft position and engine speed are detected contactlessly. The distance between crankshaft position sensor and the teeth of the driven plate is fixed by the installation position. When the crankshaft is rotating, an alternating voltage is generated in the crankshaft position sensor by the teeth of the driven plate.
The leading edge of a tooth generates a positive voltage pulse and the trailing edge a negative voltage pulse. The distance from the positive to the negative voltage peak corresponds to the length of a tooth. The gap produced by 2 missing teeth results in no voltage being generated in the crankshaft position sensor. This is analyzed for detecting the TDC position:
| Engine | Recognition of TDC position of cylinder |
|---|---|
| 111 | 1 and 4 |
| 119, 104, 112, 113 | 1 and 6 |
| 120 | Right hand cylinder bank: 1 and 6; Left cylinder bank: 7 and 12. |
| 137 | 1 and 7 |
Issues
M-B CPS often fail completely or become intermittent. If the crankshaft position sensor fails, it will not send information about the position of the crankshaft and speed of the engine RPMs to the ECU. As a result, the ECU doesn't know when to fire the spark plugs and how to adjust the fuel mixture. This can cause your car to stall or hesitate to start.
If you have been experiencing stalling or no start conditions, a failed crankshaft position sensor is often the problem.
Symptoms of fault:
- The engine may crank, but it will not start (starting problems are initially random, but more frequent when the engine is hot).
- The engine cranks longer in order to get it to start.
- Car runs for a short time, or until it gets warm and then it dies.
- Poor acceleration, engine vibrations, poor throttle response, bad fuel economy.
- Impact on transmission shifting. In some cases, it can cause the transmission to go into limp mode.
Hint: If you are stuck on a parking lot and the car will not start, let the car cool down at least 30 minutes and then try again.
Often when the car gets hot, the sensor gets hot and the sensor's resistance goes open circuit, thus the car dies. Once the engine and sensor cool down, and if you are lucky, the resistance may come back into spec, thus the car starts again.
Fault Codes
If your check engine light is on, then your ECU has recorded some sort of trouble code. You can check these codes with a diagnostic scan tool.
Codes between P0335 and P0339 correspond to crankshaft sensor problems.
This is probably the most straightforward and the most certain way to test for and identify a crankshaft sensor problem.
Unfortunately, the crankshaft sensor is usually pretty far gone by the time that the check engine light is on.
You might already be experiencing crankshaft sensor problems before the ECU has noted any sign of trouble.
| Error Code | Description |
|---|---|
| P0335 | Crankshaft Position Sensor A Circuit Malfunction (L5) |
| P0336 | Crankshaft Position Sensor A Circuit Range/Performance |
| P0337 | Crankshaft Position Sensor A Circuit Low Input |
| P0338 | Crankshaft Position Sensor A Circuit High Input |
| P0339 | Crankshaft Position Sensor A Circuit Intermittent |
Part Numbers
W220 uses magnetic impulse triggering sensor with two wires.
- CPS OE A0031532728 (Replaced by A0031532828)
- CPS OE A0031532828 (~125EUR)
- CPS BOSCH part 0261210170 (~50EUR)
- Screw N910142006001
- Pin bushing housing A1685453028
 |
 |
 |
 |
DIY Tests
The CPS can be tested by measuring its resistance and checking whether it generates voltage.
Resistance Testing
- Remove the sensor. (See section 'DIY Replacement - CPS' below.)
- Measure the resistance by attaching a multi-meter to each male pin in the sensor connector.
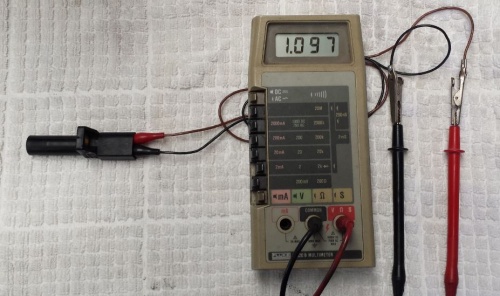
- Check the result against the manufacturer's specification. M-B WIS states for a W220 that the internal resistance of the sensor unit should be between 0.6K Ohms and 1.3K Ohms.
- Resistance of zero means that there is a short circuit.
- Infinite resistance means there is an open circuit.
- Repeat the resistance measurement while heating the sensor with a hair drier or heat gun. A CPS will often give a reading within spec when at ambient temperature but produce an open circuit after being heated slightly. The OEM (Bosch) CPS in the above figure produced a resistance of 1.097K Ohms at 25C and went open circuit when heated slightly.
- If your reading is not close to the recommended resistance, then you should replace the sensor.
Voltage Testing
- Another way to test the crankshaft sensor with a multi-meter is by checking the output voltage with the engine cranking. You will need an assistant to do this. Be very careful around moving parts as you do this.
- Probe the wiring connectors and measure the output voltage in AC millivolts. Typically, this reading is around 200 millivolts, but this can vary from vehicle to vehicle. Check the manufacturer's specifications.
- If there is no output voltage, then, obviously, your sensor is not working.
DIY Replacement
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Tools needed:
- E8 torx 1/4 socket.
- Ratchet with 6-inch 1/4 extension.
Steps:
- Remove engine cover.
- Unplug the electrical connector from the CPS sensor.
- Remove bolt using E8 torx socket.
- Install in opposite order.
Note: If a heat shield is installed, there may be too small space for hand to fit. The way around it to not actually remove the connector, but just blindly remove the E8 torx bolt and use the connector and attached cable to remove the CPS.
Resources
- http://www.doityourself.com/stry/warning-signs-of-a-bad-crankshaft-position-sensor
- http://www.mercedesmedic.com/crank-shaft-position-sensor/
- https://www.1aauto.com/content/articles/crank-sensor-testing
- http://www.benzworld.org/forums/w220-s-class/1307031-2000-s500-problem-please-help.html
- http://www.benzworld.org/forums/w220-s-class/1496096-diy-cps-write-up.html
- http://www.benzworld.org/forums/w220-s-class/1635675-how-replace-cps-crankshaft-position-sensor.html
- http://mbworld.org/forums/s-class-w220/326637-how-replace-crank-position-sensor-cps-s500.html