Headlights: Difference between revisions
(initial version) |
(→Headlamp range adjustment motors: A1408201908) |
||
| Line 148: | Line 148: | ||
* E2m1 - Right headlamp range adjustment motor | * E2m1 - Right headlamp range adjustment motor | ||
* N71 - Headlamp range adjustment control module | * N71 - Headlamp range adjustment control module | ||
|} | |||
Both headlamps (left and right) contain headlamp range adjustment motor part number A1408201908. | |||
{| | |||
|[[File:A1408201908_side.jpg|thumb|none|A1408201908 side.]] | |||
|[[File:A1408201908_connector.jpg|thumb|none|A1408201908 connector socket.]] | |||
|[[File:A1408201908_back.jpg|thumb|none|A1408201908 back.]] | |||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 22:53, 18 June 2016
Description - Head Lights
Facelift
Pre-facelift
Bi-Xenon headlamp
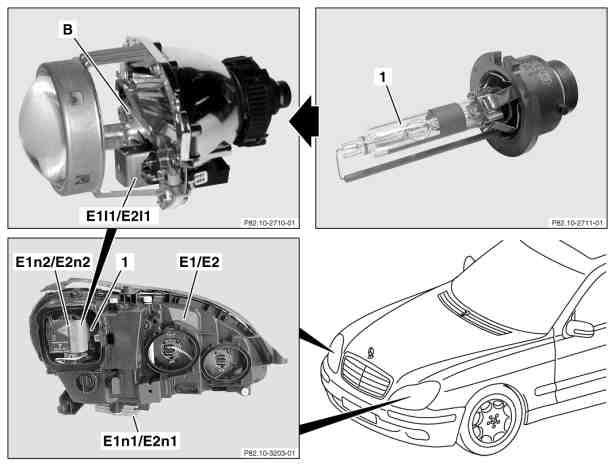
The headlamps in W220 facelift differ from the previous xenon headlamps on account of their entirely new lighting technology development, which the xenon light uses for low and high beam lights. The new lighting technology, known as Bi-Xenon, is located in the outer headlamps.
When the low beam lamps are switched on the xenon headlamp control module (E1n1, E2n1) activates the xenon headlamp control module and ignition module (E1n2, E2n2) via the control voltage within a few milliseconds. A high-voltage surge from the ignition device ignites the xenon lamps, and in doing so an electric arc is formed between the electrodes. If an electric arc of sufficient stability is detected the control circuit switches the control modules (E1n1, E2n1) over to power-limiting mode.
With the bi-xenon headlamps, the light generated in the previous manner in a gas discharge lamp (D2S lamp) travels directly through the optical system without being reflected.
A voltage converter generates the required voltage for the reliable function of the xenon headlamp.
For technical reasons the xenon lamp has a timed startup characteristic. After switch on, 50 % of the luminosity is reached within 1 to 2 seconds and full luminosity is achieved after another approx. 30 seconds.
The entire luminous flux is made available for the high-beam lights. When switching over to low-beam operation a screen is moved into position between the gas-discharge lamp and the lens, which covers up the luminous flux directed into the distance and thus helps to prevent oncoming traffic from being dazzled.
The shield (B) is controlled electro-mechanically by the solenoids in the right and left high beams (E1l1, E2l1).
Xenon headlamp control module

The xenon headlamp control module (E1n1, E2n1) activates the xenon headlamp control module and ignition module (E1n2, E2n2) via the control voltage and regulates the voltage supply to the xenon headlamps.
Xenon headlamp ignition unit
The xenon headlamp ignition device, (E1n2, E2n2) ignites the xenon lamps by means of a high-voltage surge.
Headlamp range control (HRC)
Electric headlamp range adjustment is required by law for vehicles with xenon headlamps to prevent dazzling oncoming traffic. The headlamp range adjustment automatically keeps the inclination angle of the low beams within the legally defined limit regardless of how the vehicle is loaded.
The headlamp range adjustment control module utilizes the signals from the level sensors on the front and rear axles for control and adjustment of the low beams. The pneumatic suspension control module processes the signals from the level sensors and transfers these to the headlamp range adjustment control module via the data bus (CAN). The headlamp range adjustment control module compares the signals with the headlamp adjustment and, if necessary actuates the headlamp range adjustment motors in the headlamps to correct the angle of inclination.
In addition to the signals from the level sensors the headlamp range adjustment control module also processes a wheel speed signal proportional to the vehicle speed transferred on the data bus from the ASR/ESP control module. Evaluation of this wheel speed signal indicates to the headlamp range adjustment control module whether the vehicle is driving at constant speed, accelerating or decelerating. At constant vehicle speed the headlamp range adjustment operates in the "static mode" with minimum headlamp motor adjustment speed. During acceleration or deceleration the "dynamic mode" with high adjustment speed is actuated.
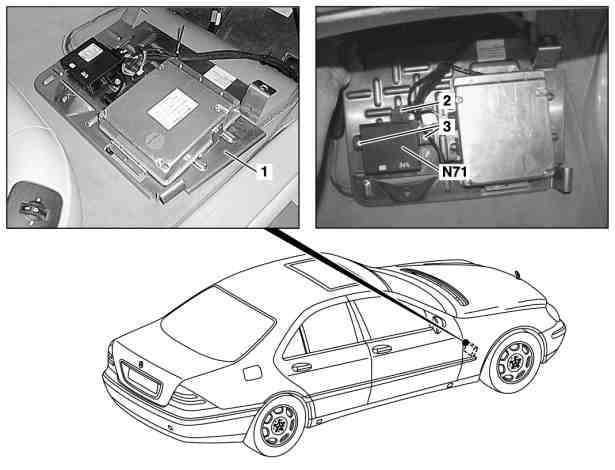
Headlamp range adjustment control module
|
|
The control module evaluates the signals from the pneumatic suspension control modules and ABS/ASP control modules as well as the headlamp range adjustment motors. It actuates the headlamp range adjustment motors depending on the vehicle load, vehicle status and position of the headlamps.
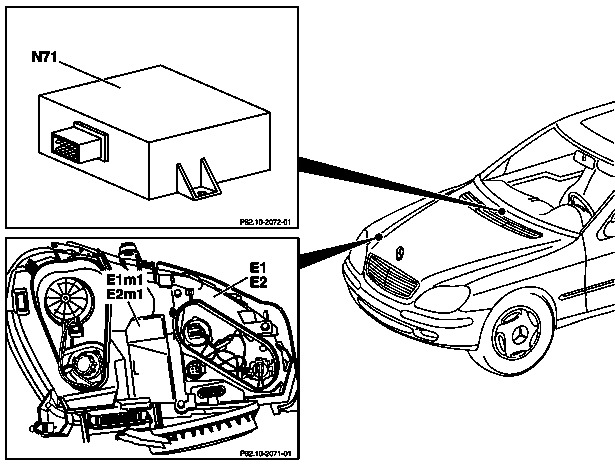
Headlamp range adjustment motors
The headlamp range adjustment motors in the left and right headlamps adjust the inclination angle of the reflectors depending on the actuation by the control module. The position of the reflectors is indicated to the control module by potentiometers in the motors.
|
|
Both headlamps (left and right) contain headlamp range adjustment motor part number A1408201908.
 |
 |
 |