Evaporative Emission Control System (EVAP)
The Evaporative Emission Control System (EVAP) is used to prevent gasoline vapors from escaping into the atmosphere from the fuel tank and fuel system at all times.
A typical system consists of the fuel tank, an EVAP vapor storage canister full of charcoal, valves, hoses and a sealed fuel tank gas cap. The EVAP system is designed to stop fuel system fumes from leaking directly into the atmosphere. Vent lines from the fuel tank pass vapors to the vapor canister, where they are trapped and stored until the engine is started. When the engine is warm and the vehicle is going down the road, the PCM then opens a purge valve allowing the vapors to be drawn from the storage canister into the intake manifold. The fuel vapors are then burned in the engine along with the air/fuel mixture.
Note that due to the legal regulation, vehicles for the USA market have a more advanced EVAP system with the benefit that it
Fuel evaporation control system function
|
Shown on engine 119
|
|
The fuel evaporation control system prevents fuel vapors escaping to atmosphere. This is done by storing the fuel vapors temporarily in the activated charcoal canister.
When the engine is running, the fuel vapors stored in the activated charcoal canister are drawn off through the purge control valve and combusted in the engine. The activated charcoal canister is purged (re-generated) at:
- Coolant temperature > 70 °C
- Blocking time after engine start elapsed, approx. 2 minutes
- Engine not in deceleration mode
The purge quantity is controlled by the ME-SFI control unit operating the purge control valve. The purge quantity is determined by constantly opening and closing the purge control valve for on and off periods of various lengths.
The idle speed control prevents changes in engine speed resulting from purging. A richer or leaner fuel-air mixture is produced in line with the charge of the activated charcoal canister with fuel vapors.
Air admission to fuel tank. Air is admitted through the activated charcoal canister. This is done through the activated charcoal canister, whereby air is drawn out of the vent/breather line or fuel vapors are drawn from the activated charcoal canister into the fuel tank.
Air release from fuel tank. The fuel tank is vented through the activated charcoal canister. The fuel vapors flow to the activated charcoal canister, where they are stored or drawn into the intake manifold in case of simultaneous regeneration.
Vent valve. On vehicles fitted with a vent valve the fuel tank is vented from a pressure of 30 to 50 mbar, and air admitted at a vacuum of 1 to 16 mbar. In addition, this prevents overfilling the fuel tank.
USA as of MY 98. During refueling the fuel vapors are collected at the filler neck and passed to the activated charcoal filter (ORVR = Onboard Refueling Vapor Recovery). Large activated charcoal canister.
Engines with charging (compressor or turbocharger). A check valve in the purge line prevents the boost pressure building up toward the activated charcoal canister.
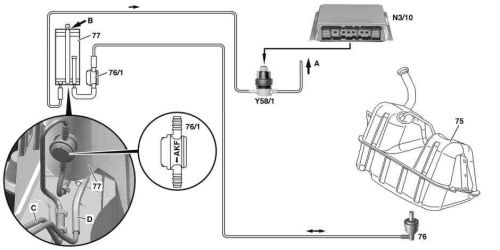
Model 215 from chassis no. A046659 (approx. 23.3.05), without USA and model 220 from chassis no. 469233 (ca. 23.3.05), without USA with ski bag (Code 282) or cooling compartment in rear backrest (Code 308) or with retrofitted additional vent valve (76/1):
The additional vent valve (76/1) prevents the vacuum from the intake manifold passing over the activated charcoal canister through to the fuel tank for enabled purging. For this purpose, the valve closes as soon as a membrane is pressurized with vacuum pressure from the activated charcoal canister. If excess pressure or vacuum pressure affects the other valve connection, it opens immediately. This means aeration/venting of the fuel tank is then possible in an unlimited fashion via the standard vent valve (76).
Pay attention to the installation position of the vent valve (76/1). Check aeration at the activated charcoal canister for contamination (e.g. dust, spider's webs).
Fuel tank ventilation system
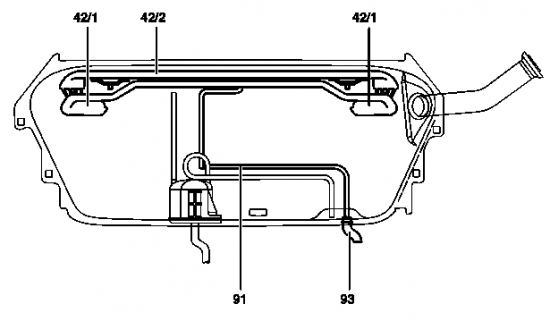
Shown on model 210.0 without ski bag (through-loading feature):
Function. The ventilation system consists of a central pipe (42/2) with an interruption vessel (42/1) at each end. The interruption vessels prevent fuel escaping along the vent line. The vent line (91) runs from the central pipe to the vent hose (93). On vehicles fitted with a gasoline engine, the vent hose (93) runs to the activated charcoal canister. As of approx. 7/98 a vent valve is integrated in the vent line to the activated charcoal canister (without USA).
On-board refueling vapor recovery function (USA up to 2000/08/31)
Task:
- The legislator requires, that the refueling gases in the vehicle are collected (ORVR = Onboard Refueling Vapor Recovery).
- Separate fuel and refueling gases to prevent fuel from flowing into the activated charcoal canister due to inappropriate refueling or a defective nozzle.
- Ending refueling when the refueling nozzle switches off and the fuel tank is full! On no account overfilling fuel tank as a result of refueling nozzle being switched on several times.
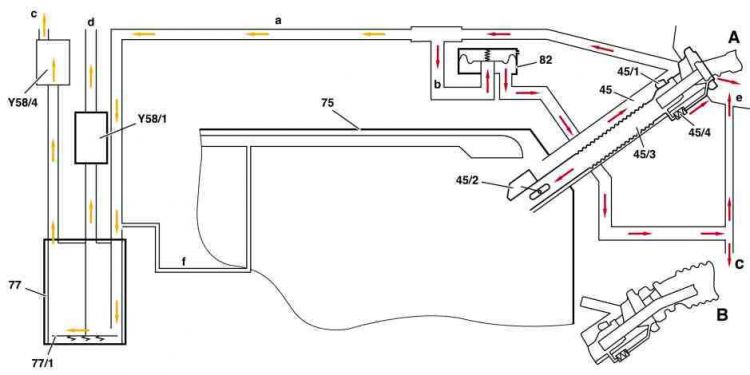
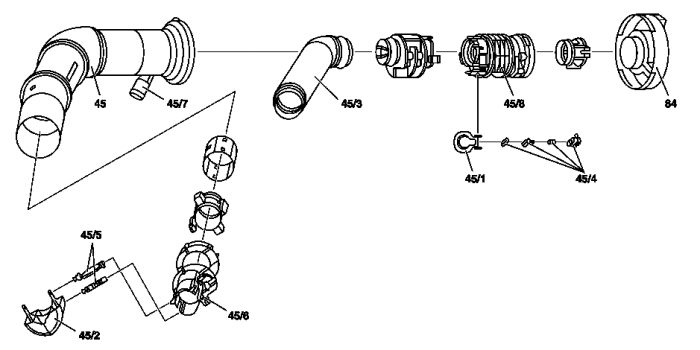
Function: The fuel vapors are recovered at the filler neck (45) and passed along a ventilation hose (a) to the activated charcoal canister. An insert inserted in the filler neck prevents, that when refueling fuel flows to the activated charcoal canister. To do this the fuel vapors in the filler neck are diverted several times in order to separate the gases from the fuel. The connection to the activated charcoal canister is shut off by a flap (45/1) when driving. It is opened by the gasoline pump nozzle when refueling.
Additional measures if fuel tank is overfilled:
- If the fuel tank is full, the float (45/2) closes with flap the filler neck below. This ensures that the refueling nozzle shuts off more rapidly and overfilling is largely prevented.
- A too high level of fuel in the filler neck presses open the pressure relief valve (45/4). Fuel flows to atmosphere at the nozzle. End refueling! On nozzles fitted with rubber boot (B) this overflowing is no longer recognizable.
- A too high pressure in the ORVR vent line (a) acts on the diaphragm in the pressure relief valve (82). If the diaphragm lifts off because of excessively high pressure, the pressure is released at the fuel tank recess (e) and below the wheelhouse to atmosphere (c). End refueling!
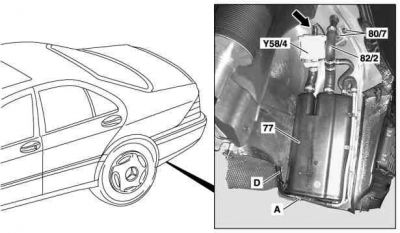
- If the pressure is too high in the activated charcoal canister (77), the pressure relief valve (77/1) opens. The pressure is reduced through the activated charcoal canister shutoff valve (Y58/4) to atmosphere (c).
Fuel filler neck with cap (USA)
The fuel filler neck (45) runs through the right, rear wheelhousing to the fuel tank. It has an inserted insert and connection for collecting fuel vapors when refueling. The insert which is inserted in the filler neck prevents, that fuel flows to the activated charcoal canister due to inappropriate refueling.
The fuel vapors in the filler neck are diverted several times in order to separate the gases from the fuel. The connection to the activated charcoal canister is shut off by a flap (45/1) when driving by means of the top insert. It is opened by the gasoline pump nozzle when refueling. When the fuel tank is full, a float closes a flap at the bottom insert. The filler neck is filled rapidly and the gasoline pump nozzle switches off.
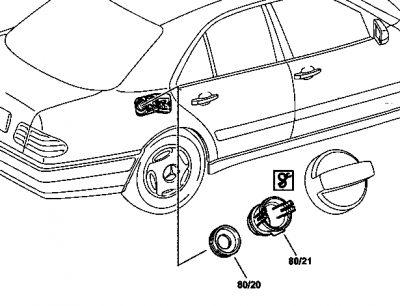
Replacing damaged nozzle gasket in the tank filler neck
- Check the lip of the nozzle gasket (80/20)
- Replace the nozzle gasket (80/20) if the lip of the nozzle (80/20) is damaged. Release the guide sleeve (80/21) using pliers (W210589013700) and take it out.
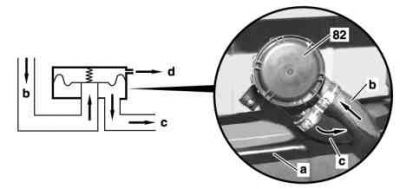
Pressure relief valve (USA)
The task of the pressure relief valve (also known as safety valve) is limiting the pressure in the ORVR vent line if fuel tank overfilled or if gasoline pump nozzle faulty (does not switch off).
The pressure relief valve consists of a housing with internal diaphragm which seals off the line to the pressure relief valve by means of a spring.
The diaphragm lifts off at a pressure of approx. 60 to 90 mbar. The fuel overflow line to atmosphere opens. Air is admitted to the diaphragm chamber.
The pressure relief valve is located below rear shelf.
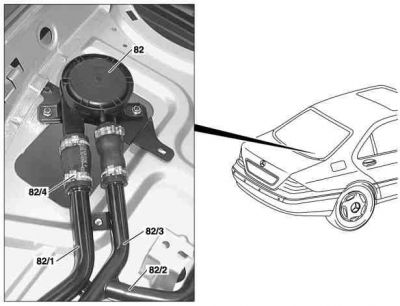
Remove/install pressure relief valve
|
Shown on model 220:
|
- Remove rear shelf
- Detach fuel hose of fuel overflow line (82/1) and fuel hose of vent line (82/3) at pressure relief valve (82). Replace hose clip (82/4).
- Remove pressure relief valve (82). Take out complete with bracket.
- Install in the reverse order
Purge control valve actuation function
For controlling the purge quantity the purge control valve is actuated at the ground side by the ME-SFI control unit by means of a pulse width-modulated signal. The purge quantity is determined by constantly opening and closing the purge control valve for on and off periods of various lengths.
The frequency of the pulse width modulation signal is selected from a speed-dependent characteristic in such a way, that all cylinders are uniformly supplied with fuel vapors.
The purge control valve is actuated when the engine is at operating temperature, but not in the deceleration mode.
The following information is processed in the ME-SFI control unit:
- Engine speed
- Air mass (boost pressure in supercharged engines)
- Coolant temperature
- Intake air temperature (charge air temperature in supercharged engines)
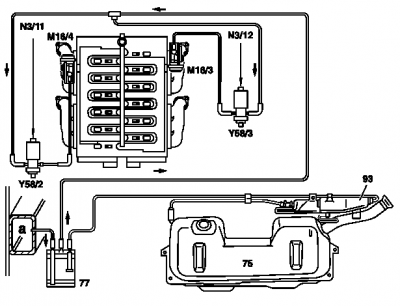
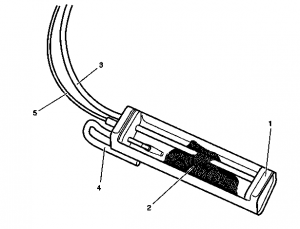
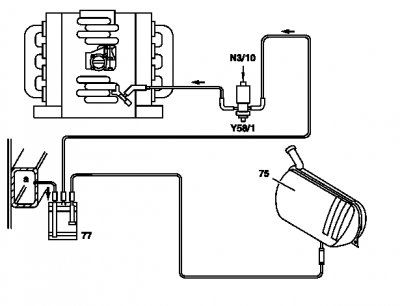
Activated charcoal canister
The task of the activated charcoal canister is ventilation and deventilation of the fuel tank and storing the fuel vapors temporarily for subsequent purging.
The hausing of the activated charcoal canister is filled with activated charcoal granulate, divided into different chambers by intermediate walls in order to achieve optimal flow through the activated charcoal. USA with ORVR: Quantities of around 2.7 to 3.5 l.
The fuel vapors released from the fuel tank (USA with ORVR or when refueling) are bonded to the activated charcoal. When purging is activated, they are drawn in by the engine and combusted. The activated charcoal is completely regenerated in the ideal case. The ventilation and deventilation of the fuel tank takes place over the activated charcoal canister.
The activated charcoal canister is located at the rear in the rear left wheelhouse.
|
|
|
USA with ORVR:
|
|
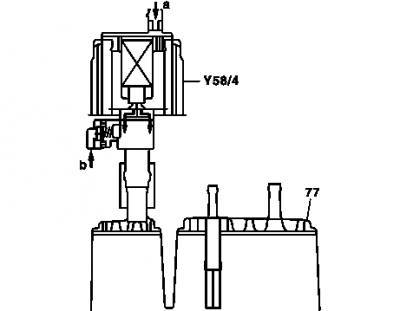
Activated charcoal canister shutoff valve (USA)
|
Shown in the design of model 210:
|
The task of the activated charcoal canister shutoff valve is to close the ventilation of the activated charcoal canister for a leakage test of the fuel system.
The shutoff valve contains a solenoid which closes the valve when energizing. Additionally a mechanical safety valve is installed.
The shutoff valve is located on the top at the vent connection of the activated charcoal canister.
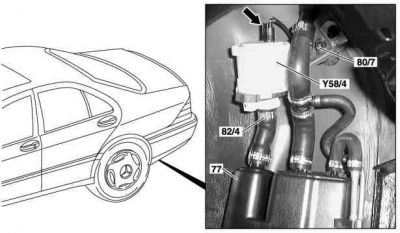
Remove/install shutoff valve
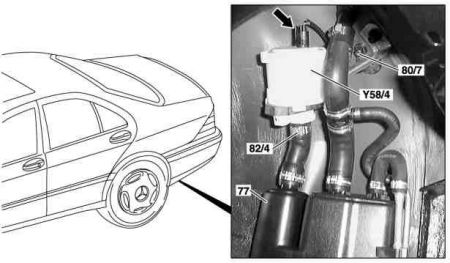
|
Shown on model 220:
|
- Remove rear left wheelhousing liner
- Detach connector (Arrow)
- Unscrew plastic nuts (80/7)
- Replace hose clip (82/4)
- Take out shutoff valve (Y58/4)
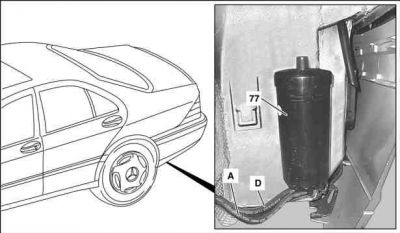
Remove/install activated charcoal canister
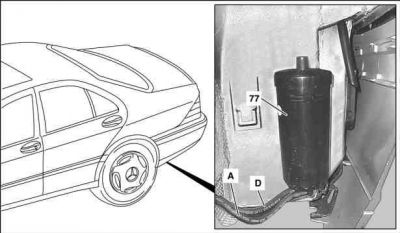
|
Shown on MODEL 220
|
- Raise vehicle.
- Remove rear left wheelhousing liner
- Detach activated charcoal canister - purge control valve line (A) and vent valve line - activated charcoal canister to fuel tank (D) at activated charcoal canister (77)
- Remove activated charcoal canister (77). Lift up and out.
- Install in the reverse order
Remove/install activated charcoal canister (USA)
- Lift rear. Remove inner fender from rear fender.
- Detach lines at activated charcoal canister (77)
- Unplug plug socket (arrow) at shutoff valve
- Unscrew plastic nuts (80/7)
- Remove activated charcoal canister (77). Lift up and out.
- Install in the reverse order
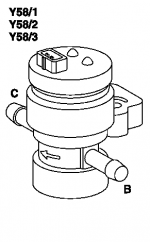
Purge control valve
The task of the purge control valve is opening and closing the connecting line between the activated charcoal canister and the intake manifold.
The purge control valve is an electric switchover valve with two line terminals and one 2-pin plug connection.
|

|
The purge control valve (Y58/1) is actuated by the ME control unit by means of a PWM signal (ground side) in line with the operating condition of the engine. If purging is actuated, the passage from the activated charcoal canister (a) to the intake manifold (b) is opened and closed.
The voltage supply to the purge control valve is performed by terminal 87.
The purge control valve is located in the engine compartment at the left wheelhouse.
|

|
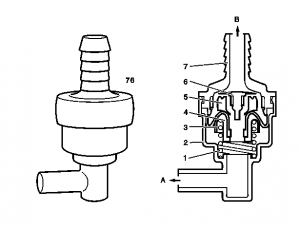
Vent valve
|
Shows model 220:
|
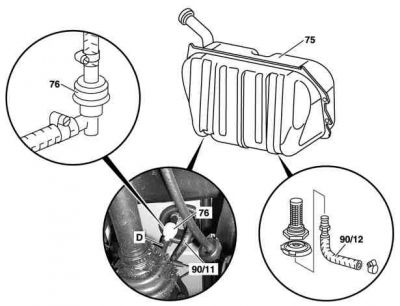
|
The task of the vent valve is the air admission and ventilation of fuel tank and prevention of overfilling. The vent valve (76) is mounted under the fuel tank in the vent line.
Fuel tank ventilation. The ventilation valve (4) opens at an overpressure of around 30 to 50 mbar. The fuel vapors flow to the activated charcoal canister.
Fuel tank aeration. The air admission valve (6) opens at a vacuum of around 1 to 16 mbar in the fuel tank. Air or fuel vapors are drawn in through the activated charcoal canister.
Refueling. The opening pressure of the vent valve (4) of approx. 30 up to 50 mbar is not achieved if the fuel tank cap is removed. The vent line to the activated charcoal canister remains closed off. This switches off the nozzle more rapidly.
Parts
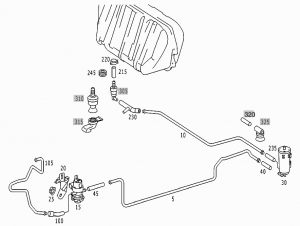
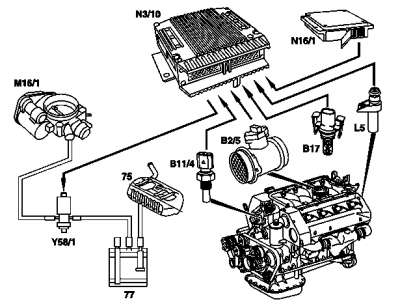
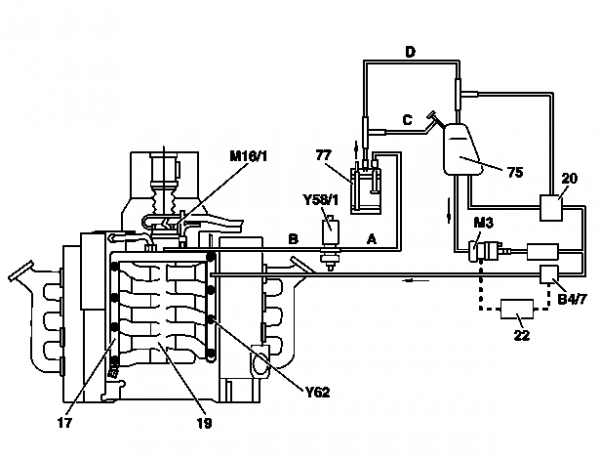
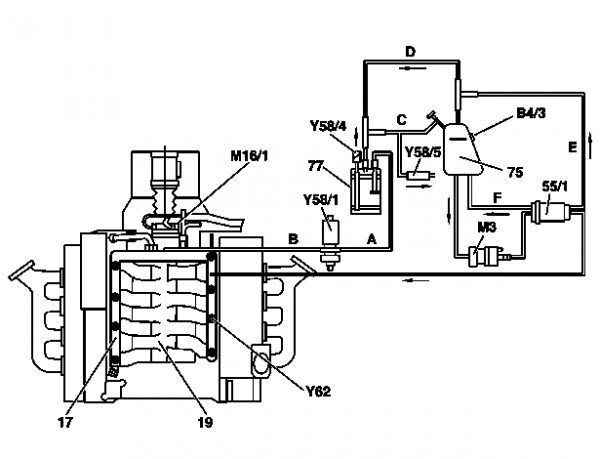
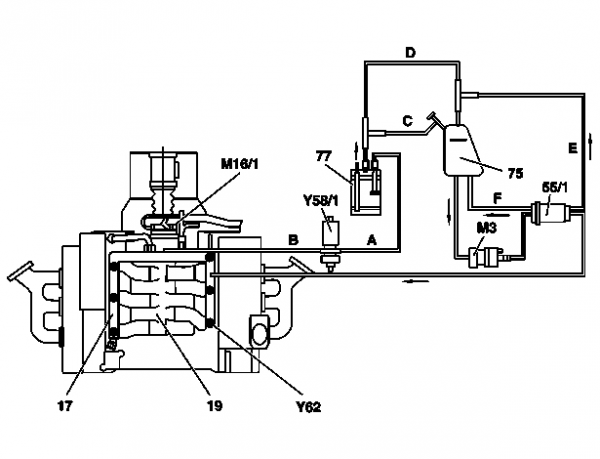
Connection diagram for evaporative emission control system (M113)
(Note: the fuel filter is incorrectly depicted in this picture. For correct depiction refer to M113 USA version picture below.)